AltFinanceDaily Around The World
September 28, 2019 Members of the AltFinanceDaily editorial team returned from Ireland this week. The Republic of Ireland will be the latest in our international series on nonbank finance. Stay tuned for our stories on that.
Members of the AltFinanceDaily editorial team returned from Ireland this week. The Republic of Ireland will be the latest in our international series on nonbank finance. Stay tuned for our stories on that.
In the meantime, be sure to check out our international coverage of:
Canada
- Canada story series
- Magazine Feature: Canada’s Alternative Financing Market Is Taking Off
- Canadian Funder Directory
Australia
- Australia story series
- Magazine Feature: Snapshot on Australia: Growth in the making
- Australia Funder Directory
Hong Kong
Mexico
PayPal Begins Offering Business Loans in Canada
July 28, 2019 PayPal has extended its popular working capital business loan program to Canada, according to company CEO Dan Schulman.
PayPal has extended its popular working capital business loan program to Canada, according to company CEO Dan Schulman.
“This quarter, we began offering our PayPal business loan product to PayPal merchants in Canada, allowing them to access financing to build and sustain their businesses,” he said during the Q2 conference call. “This follows the expansion of our business financing solutions to Germany in Q4 2018 and in Mexico earlier this year in partnership with Mexican lending platform Konfio.”
AltFinanceDaily ranked PayPal as the leading alternative small business finance company by originations in 2018. They are followed by OnDeck, Kabbage, Square, and Amazon.
Are The Bankers Taking Over Fintech?
June 27, 2019
For Rochelle Gorey, the chief executive and co-founder of SpringFour, a “social impact” fintech company, mingling with industry movers and shakers at this year’s LendIt Fintech Conference was just what the doctor ordered. “I went mainly for the networking opportunities,” Gorey told AltFinanceDaily.
SpringFour, which is headquartered in Chicago, works with banks and financial institutions in the 50 states to get distressed borrowers back on track with their debt payments. It does this by digitally linking debtors with governmental and nonprofit agencies that promote “financial wellness.
The indebted parties—more than a million of whom had referrals that were arranged by Gorey’s tech-savvy company last year—constitute not only household consumers but also commercial borrowers. “Small businesses face the same issues of cash flow as consumers, and their business and personal income are often combined,” she says. “If their financial situation is precarious, it’s super-hard to get credit, a line of credit, or a business loan.”
 Although Gorey felt “overwhelmed” at first by the throng of 4,000 conference-goers at Moscone Center West in San Francisco—roughly the same number as attended last year, conference organizers assert— her trepidation was short-lived. It wasn’t too long before she was in circulation and having chance encounters and serendipitous interactions, she says, with “all the right people at the workshops and at the tables in the Expo Hall.”
Although Gorey felt “overwhelmed” at first by the throng of 4,000 conference-goers at Moscone Center West in San Francisco—roughly the same number as attended last year, conference organizers assert— her trepidation was short-lived. It wasn’t too long before she was in circulation and having chance encounters and serendipitous interactions, she says, with “all the right people at the workshops and at the tables in the Expo Hall.”
Armed, moreover, with a “networking app” on her mobile phone, Gorey was able to arrange targeted meetings, scoring roughly a dozen, 15-minute tete-a-tetes during the two-day breakout sessions. These included audiences with community bankers, financial technology companies, and “small-dollar” lenders. “And it went both ways,” she says. “I had people reaching out to me”—just about everyone, it seemed, appeared receptive to “finding ways to boost their customers’ financial health.”
Gorey’s success at networking was precisely the experience that the event’s planners had envisioned, says Peter Renton, chairman and co-founder of the LendIt Fintech Conference. Organizers took pains to make schmoozing one of the key features of this year’s gathering. Not only did LendIt provide attendees with a bespoke networking app, but planners scheduled extra time for meet-ups. “We had around 10,000 meetings set up by the app,” Renton says, “about double the number of last year.”
AltFinanceDaily did not attend the LendIt USA conference on the West Coast this year. But the publication sought out more than a half-dozen attendees—including several financial technology executives, a leading venture capitalist, a regulatory law expert, and the conference’s top administrators—to gather their impressions. While informal and manifestly unscientific, their responses nonetheless yielded up several salient themes.
The popularity—and effectiveness—of networking was a key takeaway. Most seized the opportunity to rub elbows with influential industry players, learn about the hottest startups, compare notes, and catch up on the state of the industry. Most importantly, the event presented a golden opportunity to make the introductions and connections that could generate dealmaking.
“My goal this year was to strike more partnerships with lenders and fintech companies,” says Levi King, chief executive and co-founder at Utah-based Nav, an online, credit-data aggregator and financial matchmaker for small businesses. “We had great meetings with Fiserv, Amazon, Clover Network (a division of First Data), and MasterCard,” he reports, rattling off the names of prominent financial services companies and fintech platforms.
James Garvey, co-founder and chief executive at Self Lender, an Austin-based fintech that builds creditworthiness for “thin file” consumers who have little or no credit history, said his goal at the conference was both to serve on a panel and “meet as many people as I could.”
Self Lender is in its growth stage following a $10 million, series B round of financing in late 2018 from Altos Ventures and Silverton Partners. Garvey reports having meetings with Bank of America and venture capitalist FTV Capital “over coffee” as well as F-Prime Capital, another venture capitalist. “It’s just about building a relationship,” he said of making connections, “so that at some point, if I’m raising money or want to partner, I can make a deal.”
There was a concerted effort to recognize women, as evidenced by a packed “Women in Fintech” (WIF) luncheon that drew roughly 250 persons, 95% of whom were women. (“Many men are big supporters of women in fintech and we didn’t want to exclude them,” Renton says). The luncheon was preceded by a novel event—a 30-minute, ladies-only “speed-networking” session—which attracted 160 participants, reports Joy Schwartz, president of LendIt Fintech and manager of the women’s programs.
At the luncheon, SpringFour’s Gorey says, “it was empowering just to see lot of women who are senior leaders working in financial services, banks and fintechs.” The keynote speech by Valerie Kay, chief capital officer at Lending Club, was another highlight. “She (Kay) talked about taking risks and going to a fintech startup after 23 years at Morgan Stanley,” Gorey reports, adding: “It was inspiring.”
The women’s luncheon also marked the launch of LendIt’s Women In Fintech mentor program, and presentation of a “Fintech Woman of the Year” award. The recipient was Luvleen Sidhu, president, co-founder and chief strategy officer at BankMobile, a digital division of Customers Bank, based near Philadelphia, which employs 250 persons and boasts two million checking account customers.
I am honored to be the 2019 Fintech Women of the Year and thrilled that @BankMobile won Most Innovative Bank. It’s very exciting to be recognized by @LendIt Fintech with this prestigious award and I congratulate the finalists in all the categories. https://t.co/qjADuKEMrB pic.twitter.com/hFJVFw1fLS
— Luvleen Sidhu (@LuvleenSidhu) April 11, 2019
BankMobile, which also won LendIt’s “Most Innovative Bank” award, has an alliance with Upstart to do consumer lending and a partnership with telecommunications company T-Mobile. Known as T-Mobile Money, the latter service provides T-Mobile customers with access to checking accounts with no minimum balance, no monthly or overdraft fees, and access to 55,000 automated teller machines, also with no fees. (At its website, T-Mobile Money describes itself as a bank and uses the slogan: “Not another bank, a better one.”)
The impressive salute to women notwithstanding, their ranks remained fairly thin: just 733 attendees identified themselves as “female” on their registration forms, LendIt’s Schwartz says, a little more than 18% of total participants. Seventy-five of the 350 total speakers and panelists—or 21%—were female. (Schwartz also reports that another 157 registrants selected “prefer not to say” as their sexual orientation, while 22 checked the box describing themselves as “non-conforming.”)
In LendIt’s defense, AltFinanceDaily, who caters to a similar audience, regularly reviews its readership demographics using several tools. They have consistently indicated that women make up 18% – 23% of the total, in line with what LendIt experienced at its most recent event.
By all accounts, many panels were informative, jampacked and attendees were engaged. King, who moderated a panel on regulatory changes in small business lending, which dealt with such topics as California’s commercial “truth-in-lending” law and controversial “confessions of judgment” laws, says: “They didn’t have to lock the door but the room was pretty full and people seemed to be paying attention. I didn’t see people studying their cellphones.”
The Expo Hall was teeming with budding fintech entrepreneurs, financial services companies and multiple vendors hawking their wares. But as numerous fintechs were angling to forge lucrative symbiotic relationships with banks, some participants—even those who were hailing the conference for its networking and deal-making opportunities—lamented the heavy presence of the establishment.
The banks’ ubiquitousness especially vexed Matthew Burton, a partner at QED Investors, an Arlington, (Va.)-based, venture capital firm and a veteran fintech entrepreneur. Before signing on with QED last year, Burton had been the co-founder of Orchard Platform, an online technology and analytics vendor for fintech and financial services companies which was purchased by fintech lender Kabbage.
Not only did bankers seem to playing a more prominent role at the LendIt conference, Burton notes, but “big four” accounting firm Deloitte had signed on as a major sponsor. “The energy level seemed a bit lower than in past years,” Burton told AltFinanceDaily. “It’s not like people were depressed but it wasn’t bubbling with excitement. A couple of years ago we thought all these new fintechs would replace the banks,” he explains. “Now the discussion is over how to partner and collaborate with banks. It’s not as exciting as when everyone thought banks were dinosaurs.
“I couldn’t really tell if there were more bankers attending this year,” Burton adds, “but it sure felt like it.”
King, the Nav executive, told AltFinanceDaily: “It was a little bit subdued. I don’t know if it was nervousness about the economy or politics, but the subject of risk came up more often in side conversations with venture-backed businesses and banks and alternative fintech lenders. One large bank we deal with,” he adds, “told me it’s spending most of its time working on risk.”
Cornelius Hurley, a Boston University law professor and executive director of the Online Lending Policy Institute who participated in a standing-room-only session on state and federal fintech regulation, declares: “I’ve been to three of their conferences, including one in New York, and I would say that this one did not have as much pizzazz. It may be that the industry is maturing.”
For his part—when asked whether there was a palpable absence of passion this year—LendIt’s Renton told AltFinanceDaily: “I would say that it felt more businesslike. Fintech has had a lot of hype and we have had conferences that were ridiculously over-hyped in 2015 and 2016. And in 2017 (the mood) was much more somber. This one felt optimistic and businesslike.”
There were 750 bankers in attendance, almost one in five participants. “The number of bankers was not up significantly” over last year, Renton says, “but the seniority of the bankers was higher. We worked very hard to get senior bankers to attend this year.”
Renton was bullish on the closer ties developing between nonbank online lenders and banks. That was reflected as well in the several panels exploring ways to develop partnerships between the two sides. He noted that a session called “How Banks are Matching Fintechs on Speed of Funding and User Experience” drew a heavy crowd. “It brought more bankers than we’ve ever had before,” Renton says.
Moderated by Brock Blake, founder and chief executive at the fintech Lendio, the panel was composed of three bankers: Ben Oltman, the Philadelphia-area head of digital lending and partnerships at Citizens Bank; Gina Taylor Cotter, a senior vice-president at American Express (the highest-ranking woman at the company); and Thomas Ferro, a senior marketing manager at Bank of America. “The banks came to LendIt not just to learn but to decide whom they’re going to partner with,” Renton says. “Fintechs need banks and banks need fintechs. That is the narrative you hear on both sides.”
(Asked whether any banks sponsored this year’s conference, Renton replied: “They are not sponsoring yet in any number but we are working on that.”)
OnDeck, a top-tier fintech lender to small-businesses in the U.S., which has been making forays abroad to Australian and Canadian markets, is an enthusiastic champion of the fintech-bank union. So much so that it claimed LendIt’s “Most Promising Partnership” award for the cooperative relationship it struck with Pittsburgh-based PNC Bank, which uses OnDeck’s platform to make small business loans. (Among the partnerships that OnDeck-PNC beat out: Gorey’s SpringFour, which was named a finalist in the competition for its association with BMO Harris Bank.)
“We were the first fintech lender to strike a true platform relationship with a bank,” Jim Larkin, head of corporate communications at OnDeck says, noting that the PNC deal follows on the New York-based fintech’s similar, innovative arrangement with J.P. Morgan Chase. “Others may do referrals,” he explains. “What we do is actually provide the underlying platform to accelerate a bank’s online lending capabilities. We deliver the software and expertise to construct the right type of online lending engine.”
Meanwhile, there was avid interest about the stock performance of publicly traded fintechs—for example, Square and GreenSky—both of which had seen their share prices tumble and then recover.
Burton noted that, among venture-backed firms, the most excitement seemed to be coming from Latin America. “Everyone was very bullish on a Mexican company, Credijusto, an alternative small business lender that was written up the in the Wall Street Journal,” he says. “It’s not going public yet but it had a large debt-and-equity raise of $100 million from Goldman Sachs. And SoftBank Group announced a $5 billion Latin American tech fund.
“There was a lot of talk,” he adds, “about how money was flowing into Mexico and Brazil.”
OnDeck Slips To #3 in Tight Pack of Top Small Business Lenders
May 3, 2019 With most 2019 Q1 earnings in for public companies, the industry’s biggest lenders are off to the races. Square reported on Wednesday that Square Capital, its business lending arm, originated $508 million in loans in the first quarter of the year. Meanwhile, OnDeck originated $636 million this quarter, according to its earnings report released yesterday. Kabbage, which is not a public company, has been trailing very closely behind OnDeck for the last few years but someone familiar with the company said that Kabbage’s originations in the first quarter of this year surpassed OnDeck’s.
With most 2019 Q1 earnings in for public companies, the industry’s biggest lenders are off to the races. Square reported on Wednesday that Square Capital, its business lending arm, originated $508 million in loans in the first quarter of the year. Meanwhile, OnDeck originated $636 million this quarter, according to its earnings report released yesterday. Kabbage, which is not a public company, has been trailing very closely behind OnDeck for the last few years but someone familiar with the company said that Kabbage’s originations in the first quarter of this year surpassed OnDeck’s.
Then there is PayPal, which has not released official origination numbers for 2019 Q1. But earlier statements from PayPal that they had surpassed a billion dollars in quarterly small business funding in 2018 (already more than OnDeck), would put it in the #1 slot for originations. Additionally, a comment made by PayPal CEO Dan Schulman during the company’s earnings call last week implied that its Q1 2019 earnings are again over a billion dollars.
PayPal’s estimated originations number represents its US and international originations, including their business financing products available in the UK, Australia, Germany and Mexico. Likewise, OnDeck’s number represents originations from the US along with its smaller markets in Australia and Canada.
Square Capital operates exclusively in the US, so its originations number is US-only. And Kabbage’s undisclosed estimated originations number represents purely US originations.
| Company Name | 2019 Q1 Funding Volume |
| PayPal | $1,000,000,000+ |
| Kabbage | $650,000,000* |
| OnDeck | $636,000,000 |
| Square | $508,000,000 |
Open Banking — A U.S. Pipe Dream or Near-Term Reality?
December 18, 2018 Some alternative funders are anxious for “open banking” to become the gold standard in the U.S., but achieving widespread implementation is a weighty proposition.
Some alternative funders are anxious for “open banking” to become the gold standard in the U.S., but achieving widespread implementation is a weighty proposition.
Open banking refers to the use of open APIs (application program interfaces) that enable third-party developers to build applications and services around a financial institution. It’s a movement that’s been gaining ground globally in recent years. Regulations in the U.K., a forerunner in open banking, went into effect in January, while several other countries including Australia and Canada are at varying stages of implementation or exploration.
For the U.S., however, the time frame for comprehensive adoption of open banking is murkier. Industry participants say the prospects are good, but the sheer number of banks and the fragmented regulatory regime makes wholesale implementation immensely more complicated. Nonetheless, industry watchers see promise in the budding grass-roots initiative among banks and technology companies to develop data-sharing solutions. Regulators, too, have started to weigh in on the topic, showing a willingness to further explore how open banking could be applied in U.S. markets.
Open banking “is a global phenomenon that has great traction,” says Richard Prior, who leads open banking policy at Kabbage, an alternative lender that has been active in encouraging the industry to develop open banking standards in the U.S. “It’s incumbent upon the U.S. to be a driver of this trend,” he says.
The stakes are particularly high for alternative lenders since they rely so heavily on data to make informed underwriting decisions. Open banking has the potential to open up scores of customer data and significantly improve the underwriting process, according to industry participants.
“Open banking massively enables alternative lending,” says Mark Atherton, group vice president for Oracle’s financial services global business unit. What’s missing at the moment is the regulatory stick to ensure uniformity. Certainly, data sharing is gradually becoming more commonplace in the U.S. as banks and fintech companies increasingly explore ways to collaborate. But even so, banks in the U.S. are currently all over the map when it comes to their approach to open banking, posing a challenge for many alternative lenders. Many alternative lenders would like to see regulators step in with prescriptive requirements so that open banking becomes an obligation for all banks, as opposed to these decisions being made on a bank-by-bank basis. Especially since many consumers want to be able to more readily share their financial information, they say.
“It will create huge value to everyone if that data is more accessible,” says Eden Amirav, co-founder and chief executive of Lending Express, an AI-powered marketplace for business loans.
Some global-minded banks like Citibank have been on the forefront of open banking initiatives. Spanish banking giant BBVA is also taking a proactive approach. In October, the bank went live in the U.S. with its Banking-as-a-Service platform, after a multi-month beta period. Also in October, JPMorgan Chase announced a data sharing agreement with financial technology company Plaid that will allow customers to more easily push banking data to outside financial apps like Robinhood, Venmo and Acorns.
There are several other examples of open banking in action. Kabbage customers, for instance, authorize read-only access to their banking information to expedite the lending process through the company’s aggregator partners, says Sam Taussig, head of global policy at Kabbage.

Also, companies such as Xero and Mint routinely interface with banks to put customers in control of their financial planning. And companies like Plaid and Yodlee connect lenders and banks to help with processes such as asset and income verification.
Some banks, however, are more reticent than others when it comes to data sharing. And with no regulatory requirements in place, it’s up to individual banks how to proceed. This can be nettlesome for alternative lenders trying to get access to data, since there’s no guarantee they will be able to access the breadth of customer data that’s available. “As an underwriter, you want the whole financial picture, and if data points are missing, it’s hard to make appropriate lending decisions,” Taussig says.
The problem can be particularly acute among smaller banks, industry participants say. While the quality of data you can get from one of the money-center banks is quite good, “as you go down the line, it becomes a little less consistent,” says James Mendelsohn, chief operating officer of Breakout Capital Finance. For these smaller banks, the issue is sometimes one of control. There’s a feeling among some community banks, that “if I make it easier for my small business customers to get loans elsewhere, I’m done,” says Atherton of Oracle.
Absent regulatory requirements, alternative lenders are hoping that this initial hesitation among some banks changes over time as they continue to gain a better understanding of the market opportunity and as more of their counterparts become open to data sharing through APIs.
Open banking could be a boon for banks in that it would enable them to service customers they probably couldn’t before, says Jeffrey Bumbales, marketing director at Credibly, which helps small and mid-size businesses obtain financing. Open banking makes for a “better customer experience,” he says.
One challenge for the U.S. market is the hodgepodge of federal and state regulators that makes reaching a consensus a more arduous task. It’s not as simple here as it may be in other markets that are less fragmented, observers say.
Major rule-making would be involved, and there are many issues that would need attention. One pressing area of regulatory uncertainty today is who bears the liability in the event of a breach—the bank or the fintech, says Steve Boms, executive director of the Northern American chapter of the Financial Data and Technology Association. Existing regulations simply don’t speak to data connectivity issues, he says.
To be sure, policymakers have started to give these matters more serious attention, with various regulators weighing in, though no regulator has issued definitive requirements. Still, some industry participants are encouraged to see regulators and policymakers taking more of an interest in open banking.
A recent Treasury Report, for example, notes that as open banking matures in the United Kingdom, “U.S. financial regulators should observe developments and learn from the British experience.” And, The Senate Banking Committee recently touched on the issue at a Sept. 18 hearing. Industry watchers say these developments are a step in the right direction, though there’s significant work needed, they say, in order to make open banking a pervasive reality.
“We’re seeing the pace and interest around these things picking up pretty significantly,” Boms says. Even so, it can take several years to implement a formal process. “The hope is obviously as soon as possible, but the financial services sector is a very fragmented market in terms of regulation. There’s going to have to be a lot of coordination,” Boms says.
Another challenge to overcome is customers’ willingness to use open banking. Many small business owners are more comfortable sending a PDF bank statement versus granting complete access to their online banking credentials, says Mendelsohn of Breakout Capital Finance. “There’s a lot more comfort on the consumer side than there is on the small business side. Some of that is just time,” he adds.
Certainly sharing financial data is a concern—even in the U.K. where open banking efforts are well underway. More than three quarters of U.K. respondents expressed concern about sharing financial data with organizations other than their bank, according to a recent poll by market research body, YouGov. This suggests that more needs to be done to ease consumers into an open banking ecosystem.
The topic of data security came up repeatedly at this year’s Money20/20 USA conference in Las Vegas. How to make people feel comfortable that their data is safe is a pressing concern, says Tim Donovan, a spokesman for Fundbox, which provides revolving lines of credit for small businesses. Clearly, it’s something the industry will have to address before open banking can really become a reality in the U.S., he says.
Despite these challenges, many market watchers feel open banking in the U.S. is inevitable, given the momentum that’s driving adoption worldwide. Several countries have taken on open banking initiatives and are at varying states of implementation—some driven by industry, others by regulation. Here is a sampling of what’s happening in other regions of the world:
In the U.K., for example, the implementation process is ongoing and is expected to continually enhance and add functionality through September 2019, according to The Open Banking Implementation Entity, the designated entity for creating standards and overseeing the U.K’s open banking initiative.
At the moment, only the U.K.’s nine largest banks and building societies must make customer data available through open banking though other institutions have and continue to opt in to take part in open banking. As of September, there were 77 regulated providers, consisting of third parties and account providers and six of those providers were live with customers, according to the U.K. open banking entity.
In Europe, the second Payment Services Directive (PSD2) requires banks to open up their data to third parties. But implementation is taking longer than expected—given the large number of banks involved. By some opinions, open banking won’t really be in force in Europe until September 2019, when the Regulatory Technical Standards for open and secure electronic payments under the PSD2 are supposed to be in place.
In Australia, meanwhile, the country has adopted a phase-in process to take place over a period of several years through 2021. Starting in July 2019, all major banks will be required to make available data on credit and debit card, deposit and transaction accounts. Data requirements for mortgage accounts at major banks will follow by February 1, 2020. Then, by July 1 of 2020, all major banks will need to make available data on all applicable products; the remaining banks will have another 12 months to make all the applicable data available.
For its part, Hong Kong is also pushing ahead with plans for open banking. In July, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority published its open API framework for the local banking sector. There’s a multi-prong implementation strategy with the final phase expected to be complete by mid-2019.
Singapore, by contrast, is taking a different approach than some other countries by not enforcing rules for banks to open access to data. The Monetary Authority of Singapore has endorsed guidelines for Open Banking, but has expressed its preference to pursue an industry-driven approach as opposed to regulatory mandates.
Other countries, meanwhile, are more in the exploratory phases. In Canada, the government announced in September a new advisory committee for Open Banking, a first step in a review of its potential merits. And in Mexico, the county’s new Fintech Law requires providers to provide fair access to data, and regulators there are reportedly gung-ho to get appropriate regulations into place. Still other countries are also exploring how to bring open banking to their markets.
The U.S. meanwhile, is on a slower course—at least for now. More banks are using APIs internally and have been exploring how they can work with third-party technology companies. Meanwhile, companies like IBM have been coming to market with solutions to help banks open up their legacy systems and tap into APIs. Other industry players are also actively pursuing ways to bring open banking to the market.
As for when and if open banking will become pervasive in the U.S., it’s anyone’s guess, but industry participants have high hopes that it’s an achievable target in the not-too-distant future.
Thus far, there has been little pressure for banks to adopt open banking policies, says Taussig of Kabbage. But this is changing, and things will continue to evolve as other countries adopt open banking and as pressure builds from small businesses and consumers in an effort to ensure the U.S. market stays competitive, he says. Open banking “is going to happen in the near future,” Taussig predicts.
The Seven-Minute Loan Shakes Up Washington And The 50 States
August 19, 2018 It takes seven minutes for Kabbage to approve a small-business loan. “The reason there’s so little lag time,” says Sam Taussig, head of global policy at the Atlanta-based financial technology firm, “is that it’s all automated. Our marginal cost for loans is very low,” he explains, “because everything involving the intake of information – your name and address, know-your-customer, anti-money-laundering and anti-terrorism checks, analyzing three years of income statements, cash-flow analysis – is one-hundred-percent automated. There are no people involved unless red flags go off.”
It takes seven minutes for Kabbage to approve a small-business loan. “The reason there’s so little lag time,” says Sam Taussig, head of global policy at the Atlanta-based financial technology firm, “is that it’s all automated. Our marginal cost for loans is very low,” he explains, “because everything involving the intake of information – your name and address, know-your-customer, anti-money-laundering and anti-terrorism checks, analyzing three years of income statements, cash-flow analysis – is one-hundred-percent automated. There are no people involved unless red flags go off.”
One salient testament to Kabbage’s automation: Fully $1 billion of the $5 billion in loans that it has made to 145,000 discrete borrowers since it opened its portals in 2011 were made between 6 p.m. and 6 a.m.

Now compare that hair-trigger response time and 24-hour service for a small business loan of $1,000-$250,000 with what occurs at a typical bank. “Corporate credit underwriting requires 28 separate tasks to arrive at a decision,” William Phelan, president, and co‐founder of PayNet—a top provider of small-business credit data and analysis – testified recently to a Congressional subcommittee. “These 28 tasks involve (among other things): collecting information for the credit application, reviewing the financial information, data entry and calculations, industry analysis, evaluation of borrower capability, capacity (to repay), and valuation of collateral.”
A “time-series analysis,” the Skokie (Ill.)-based executive went on, found that it takes two-to-three weeks – and often as many as eight weeks—to complete the loan approval process. For this “single credit decision,” Phelan added, the services of three bank departments – relationship manager, credit analyst, and credit committee – are required.
The cost of such a labor-intensive operation? PayNet analysts reckoned that banks incur $4,000-$6,000 in underwriting expenses for each credit application. Phelan said, moreover, that credit underwriting typically includes a subsequent loan review, which consumes two days of effort and costs the bank an additional $1,000. “With these costs,” Phelan told lawmakers, “banks are unable to turn a profit unless the loan size exceeds $500,000.”
According to the National Bureau of Economic Research, the country’s very biggest banks — Bank of America, Citigroup, J.P. Morgan Chase, and Wells Fargo—have been the financial institutions most likely to shut down lending to small businesses. “While small business lending declined at all banks beginning in 2008,” NBER’s September, 2017 report announces, “the four largest banks” which the report dubs the ‘Top Four’—“cut back significantly relative to the rest of the banking sector.”
NBER reports further that by 2010—the “trough” of the financial crisis—the annual flow of loan originations from the Top Four stood at just 41% of its 2006 level, which compared with 66% of the pre-crisis level for all other banks. Moreover, small-business lending at the “Top Four” banks remained suppressed for several years afterward, “hovering” at roughly 50% of its pre crisis level through 2014. By contrast, such lending at the rest of the country’s banks eventually bounced back to nearly 80% of the pre-crisis level by 2014.

That pullback—by all banks—continues, says Kenneth Singleton, an economics professor at Stanford University’s Graduate School of Business. Echoing Phelan’s testimony, Singleton told AltFinanceDaily in an interview: “Given the high underwriting costs, banks just chose not to make loans under $250,000,” which are the bread-and-butter of small-business loans. In so doing, he adds, banks “have created a vacuum for fintechs.”
All of which helps explain why Kabbage and other fintechs making small business loans are maintaining a strong growth trajectory. As a Federal Reserve report issued in June notes, the five most prominent fintech lenders to small businesses—OnDeck, Kabbage, Credibly, Square Capital, and PayPal—are on track to grow by an estimated 21.5 percent annually through 2021.
Their outsized growth is just one piece—albeit a major one—of fintech’s larger tapestry. Depending on how you define “financial technology,” there are anywhere from 1,400 to 2,000 fintechs operating in the U.S., experts say. Fintech companies are now engaged in online payments, consumer lending, savings and investment vehicles, insurance, and myriad other forms of financial services.
Fintechs’ advocates—a loose confederacy that includes not only industry practitioners but also investors, analysts, academics, and sympathetic government officials—assert that the U.S. fintech industry is nonetheless being blunted from realizing its full potential. If fintechs were allowed to “do their thing,” (as they said in the sixties) this cohort argues, a supercharged industry would bring “financial inclusion” to “unbanked” and “underbanked” populations in the U.S. By “democratizing access to capital,” as Kabbage’s Taussig puts it, harnessing technology would also re-energize the country’s small businesses, which creates the majority of net new jobs in the U.S., according to the U.S. Small Business Administration.
But standing in the way of both innovation and more robust economic growth, this cohort asserts, is a breathtakingly complex—and restrictive—regulatory system that dates back to the Civil War. “I do think we’re victims of our own success in that we’ve got a pretty good financial system and a pretty good regulatory structure where most people can make payments and the vast majority of people can get credit.” says Jo Ann Barefoot, chief executive at Barefoot Innovation Group in Washington, D.C. and a former senior fellow at Harvard’s Kennedy School. But because of that “there’s been more inertia and slower adoption of new technology,” she adds. “People in the U.S. are still going to bank branches more than people in the rest of the world.”

Barefoot adds: “There are five agencies directly overseeing financial services at the Federal level and another two dozen federal agencies” providing some measure of additional, if not duplicative oversight, over financial services. “But there’s no fintech licensing at the national level,” she says. And because each state also has a bank regulator, she notes, “if you’re a fintech innovator, you have to go state by state and spend millions of dollars and take years” to comply with a spool of red tape pertaining to nonbanks.
At the federal level, the current system— which includes the Federal Reserve, Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)—developed over time in a piecemeal fashion, largely through legislative responses to economic panics, shocks and emergencies. “For historical reasons,” Barefoot remarks, “we have a lot of agencies” regulating financial services.
For exhibit A, look no further than the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau created amidst the shambles of the 2008-2009 financial crisis by the 2010 Dodd-Frank Act. Built ostensibly to preserve safety and soundness, the agencies have constructed a moat around the banking system.
Karen Shaw Petrou, managing partner at Federal Financial Analytics, a Washington, D.C. consultancy, is a banking policy expert who frequently provides testimony to Congress and regulatory agencies. She wrote recently that the country’s banking sector has been protected from the kind of technological disruption that has upended a whole bevy of industries.
“The only reason Amazon and its ilk may not do to banking, brokers and insurers what they did to retailers—and are about to do to grocers and pharmacies,” she observed recently in a blog—“is the regulatory structure of each of these businesses. If and how it changes are the most critical strategic factors now facing finance.”

Cornelius Hurley, a Boston University law professor and executive director of the Online Lending Policy Institute, is especially critical of the 50-state, dual banking system. State bank regulators oversee 75 percent of the country’s banks and are the primary regulators of nonbank financial technology companies. “The U.S. is falling behind other countries that are much less balkanized,” Hurley says. “Our federal system of government has served us well in many areas in our becoming a leading civil society. It’s given us NOW (Negotiable Order of Withdrawal) accounts, money-market accounts, automatic teller machines, and interstate banking. But now it’s outlived its usefulness and has become an impediment.”
Take Kabbage, which actually avoids a lot of regulatory rigmarole by virtue of its partnership with Celtic Bank, a Utah-chartered industrial bank. The association with a regulated state bank essentially provides Kabbage with a passport to conduct business across state lines. Nonetheless, Kabbage has multiple, incessant, and confusing dealings with its bank overseers in the 50 states.
“Where the states get involved,” says Taussig, “is on brokering, solicitation, disclosure and privacy. We run into varying degrees of state legislative issues that make it hard to do business. Right now we’re plagued by what’s been happening with national technology actors on cybersecurity breaches and breach disclosures. We are required to notify customers. But some states require that we do it in as few as 36 hours, and in others it’s a couple of months. We’ve lobbied for a national breach law of four days,” he adds, which would “make it easier for everyone operating across the country.”
Then there’s the meaning of “What is a broker?’” says Taussig, who as a regulatory compliance expert at Kabbage sees his role as something of an emissary and educator to regulators and politicians, the news media, and the public. “The definitions haven’t been updated since the 1950s and now we have wildly different interpretations of brokering and solicitation,” he says. “The landscape has changed with e-commerce and each state has a different perspective of what’s kosher on the Internet.”

Washington State is a good example. It’s one of a handful of jurisdictions in which regulators confine nonbank fintechs to making consumer loans. In a kabuki dance, fintech companies apply for a consumer-lending license and then ask for a special dispensation to do small-business lending.
And let’s not forget New Mexico, Nevada and Vermont where a physical “brick-and-mortar” presence is required for a lender to do business. Digital companies, Taussig says, would have to seek a waiver from regulators in those states. “Many companies spend a lot of money on billable hours for local lawyers to comply with policies and procedures,” Taussig reports, “and it doesn’t serve to protect customers. It’s really just revenue extraction.”
All such restraints put fintechs at a disadvantage to traditional financial institutions, which by virtue of a bank charter, enjoy laws guaranteeing parity between state-chartered and federally chartered national banks. The banks are therefore able to traverse state lines seamlessly to take deposits, make loans, and engage in other lines of business. In addition, fintechs’ cost of funds is far higher than banks, which pay depositors a meager interest rate. And banks have access to the Fed discount window, while their depositors’ savings and checking accounts are insured up to $200,000.
The result is a higher cost of funds for fintechs, which principally depend on venture capital, private equity, securitization and debt financing as well as retained earnings. And that translates into steeper charges for small business borrowers. A fintech customer can easily pay an interest rate on a loan or line of credit that’s three to four times higher than, say, a bank loan backed by the U.S. Small Business Administration.
Kabbage, for example, reports that its average loan of roughly $10,000 typically carries an interest rate of 35%-36%. It’s credits are, of course, riskier than the banks’. The company does not report figures on loans denied, Taussig told AltFinanceDaily, but Stanford’s Singleton says that the fintech industry’s denial rate is roughly 50 percent for small business loans. “Fintechs have higher costs of capital and they’re also facing moderate default rates,” notes Singleton. “They’re not enormous, but fintechs are dealing with a different segment. Small businesses have much more variability in cash flows, so lending could be riskier than larger, established companies.”
 Even so, venture capitalists continue to pour money into fintech start-ups. “I’ve gone to several conferences,” Singleton says, “and everywhere I turn I’m meeting people from a new fintech company. One of the striking things about this space,” he adds, “is that there are lot of aspiring start-ups attacking very specific, very narrow issues. Not all will survive, but someone will probably acquire them.”
Even so, venture capitalists continue to pour money into fintech start-ups. “I’ve gone to several conferences,” Singleton says, “and everywhere I turn I’m meeting people from a new fintech company. One of the striking things about this space,” he adds, “is that there are lot of aspiring start-ups attacking very specific, very narrow issues. Not all will survive, but someone will probably acquire them.”
Contrast that to the world of banking. Many banks are wholeheartedly embracing technology by collaborating with fintechs, acquiring start-ups with promising technology, or developing in-house solutions. Among the most impressive are super-regionals Fifth Third Bank ($142.2 billion), Regions Financial Corp. ($123.5 billion), and BBVA Compass ($69.6 billion), notes Miami-based bank consultant Charles Wendel. But many banks are content to cater to familiar customers and remain complacent. One result is that there’s been a steady diminution in the number of U.S. banks.
Over the past ten years, fully one-third of the country’s banks were swallowed whole in an acquisition, disappeared in a merger, failed, or otherwise closed their doors. There were 5,670 federally insured banks at the end of 2017, according to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp., a 2,863-bank, 33.5% decrease from the 8,533 commercial banks operating in the U.S. in 2007.
It does appear that, to paraphrase an old expression, many banks “are going out of style.” In recent years there have been more banking industry deaths than births. Sixty-three banks have failed since 2013 through June while only 14 de novo banks have been launched. In Texas, which is known for having the most banks of any state in the country, only one newly minted bank debuted since 2009. (The Bank of Austin is the new kid on the Texas block, opening in a city known as a hotbed of technology with its “Silicon Hills.”)
One reason there’s so little enthusiasm among venture capitalists and other financial backers for investing in de novo banks is that regulators are known to be austere. “If you’re a company in the U.S.,” says Matt Burton, a founder of data analytics firm Orchard Platform Markets (which was recently acquired by Kabbage), “and you tell regulators that you want to grow by 100 percent a year – which is the scale you must grow at to get venture-capital funding – regulators will freak out. Bank regulators are very, very strict. That’s why you never hear about new banks achieving any sort of scale.”
But while bank regulators “are moving sluggishly compared to the rest of the world” in adapting to the fintech revolution, says Singleton, there are numerous signs that the status quo may be in for a surprising jolt. The Treasury Department is about to issue (possibly by the time this story is published) a major report recommending an across-the-board overhaul in the regulatory stance toward all nonbank financials, including fintechs. According to a report in The American Banker, Craig Phillips, counselor to Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin, told a trade group that the report would address regulatory shortcomings and especially “regulatory asymmetries” between fintech firms and regulated financial institutions.

Christopher Cole, senior regulatory counsel at the Independent Community Bankers Association—a Washington, D.C. trade association representing the country’s Main Street bankers—told AltFinanceDaily that, among other things, the Treasury report would likely recommend “regulatory sandboxes.” (A regulatory sandbox allows businesses to experiment with innovative products, services, and business models in the marketplace, usually for a specified period of time.)
That’s an idea that fintech proponents have been drumming enthusiastically since it was pioneered in the U.K. a few years ago, and it’s something that the independent bankers’ lobby, whose member banks are among the most threatened by fintech small-business lenders, says it too can support. Treasury’s Phillips “has said in the past that he’d like to see a level playing field,” the ICBA’s Cole says. “So if (regulators) are going to allow a sandbox, any company could be involved, including a community bank. We agree with him, of course, because we’d like to take advantage of that.”
In March, 2018, Arizona became the first state to establish a regulatory sandbox when the governor signed a law directing that state’s attorney general (and not the state’s banking regulator) to oversee the program. The agency will begin taking applications in August with approval in 90 days, says Paul Watkins, civil litigation chief in the AG’s office. Watkins told AltFinanceDaily that he’s been most surprised so far by “the degree of enthusiasm” from overseas companies. With the advent of the sandbox, he adds, “Landlocked Arizona has become a port state.”
 The OCC, which is part of the Treasury Department, may also revive its plan to issue a national bank charter to fintechs, sources say (EDITOR’S NOTE: This had not yet been implemented before this story went to print. The OCC is now accepting such applications) – a hugely controversial proposal that was put on ice last year (and some thought left for dead) when former Commissioner Thomas J. Curry’s tenure ended last spring. At his departure, the fintech bank charter faced a lawsuit filed by both the New York State Banking Department and the Conference of State Bank Supervisors. (Since then, the lawsuit was tossed out by the courts on the ground that the case was not “ripe” – that is, it was too soon for plaintiffs to show injury).
The OCC, which is part of the Treasury Department, may also revive its plan to issue a national bank charter to fintechs, sources say (EDITOR’S NOTE: This had not yet been implemented before this story went to print. The OCC is now accepting such applications) – a hugely controversial proposal that was put on ice last year (and some thought left for dead) when former Commissioner Thomas J. Curry’s tenure ended last spring. At his departure, the fintech bank charter faced a lawsuit filed by both the New York State Banking Department and the Conference of State Bank Supervisors. (Since then, the lawsuit was tossed out by the courts on the ground that the case was not “ripe” – that is, it was too soon for plaintiffs to show injury).
Taussig, the regulatory expert at Kabbage, reports that the Comptroller of the Currency, Robert J. Otting, has promised “a thumbs-up or thumbs-down” decision by the end of July or early August on issuing fintechs a national bank charter. He counts himself as “hopeful” that OCC’s decision will see both of the regulator’s thumbs pointing north.

The Conference of State Bank Supervisors, meanwhile, has extended an olive branch to the fintech community in the form of “Vision 2020.” CSBS touts the program as “an initiative to modernize state regulation of non-bank financial companies.” As part of Vision 2020, CSBS formed a 21-member “Fintech Industry Advisory Panel” with a recognizable roster of industry stalwarts: small business lenders Kabbage and OnDeck Capital are on board, as are consumer lenders like Funding Circle, LendUp and SoFi Lending Corp. The panel also boasts such heavyweights in payments as Amazon and Microsoft.
Working closely with the fintech industry is a “key component” of Vision 2020, Margaret Liu, deputy general counsel at CSBS, told AltFinanceDaily in a recent telephone interview. CSBS and the fintech industry are “having a dialogue,” she says, “and we’re asking industry to work together (with us) and bring us a handful of top recommendations on what states can do to improve regulation of nonbanks in licensing, regulations, and examinations.
“We want to know,” she added, ‘What the main friction points are so that we can find a path forward. We want to hear their concerns and talk about pain points. We want them to know the states are not deaf and blind to their concerns.”
Gale Force Twins
April 24, 2018
As Hurricane Irma swept through the Caribbean and barreled toward the Florida Keys early last September, Wendy Vila, chief executive, at Unicus Capital evacuated her home in West Palm Beach and decamped to Panama City in the Florida panhandle where “it was just a little bit rainy.”
After safely waiting out Irma, she says, her return south was precarious. The roads were strewn with tree branches and other debris. Fuel was scarce. Many gas stations were either closed or posted signs reading “No Gas.” “Restaurants had run out of food,” Vila adds, “so there was nothing to eat” along the highway.
She returned to West Palm Beach but didn’t stay long. Instead, Vila again drove west, this time across the Florida peninsula to the South Florida city of Naples, not far from where Irma had made landfall. “I went there to volunteer with Samaritan’s Purse for two days,” she says, referring to the Boone, N.C.-based Christian organization that provides humanitarian aid to people in physical need. “Things were a lot worse there than in West Palm Beach,” she reports. “A lot of trees were down, houses were flooded and people had to throw all of their belongings out onto the street.”
Meanwhile, many of the Florida merchants whom Unicus funds were distressed. “If people had no power,” Vila says, “they couldn’t function. A lot of businesses had to close down. For some merchants in the affected areas,” she adds, Unicus extended “a 90-day grace period.”

Vila’s experience with Hurricane Irma – both professionally and personally — is not an isolated one. She is among several business lenders whom AltFinanceDaily interviewed about the storm and its aftermath. This article grew out of AltFinanceDaily’s Florida networking event at the Gale Hotel in South Beach in late January. We went back to many of the attendees as well as to other business-funders in The Sunshine State and sought out their experiences before, during and after the powerful tempest.
At one point, Hurricane Irma was the strongest hurricane ever recorded in the Atlantic by the National Hurricane Center. As Irma took dead aim at Florida, it packed sustained winds exceeding 157 miles per hour, earning it the designation of a Category 5 storm, the highest and most destructive. It slammed into the Florida Keys as a Category 4 hurricane, reached the Gulf of Mexico, and then came ashore a second time on Florida’s west coast at Marco Island, just south of Naples, and began traversing the state as a Category 3 hurricane, gradually losing strength. By the time Irma exited Florida, it had been downgraded to a tropical storm. According to the National Hurricane Center, Irma caused an estimated $50 billion in damage in the U.S., making it the fifth-costliest hurricane to hit the mainland.
Financiers and brokers told personal stories of working with and assisting merchants across Florida who sought to regain their lost footing and keep from going — literally — underwater. In many cases, members of the alternative business financing community said, they were simultaneously assisting troubled merchants while they themselves struggled with Irma-occasioned troubles that ranged from inconvenience to hardship.
“I was ten days without power,” says Manny Columbie, funding manager at Axiom Financial, based in South Miami. Columbie, who lives in the residential Westchester district of Miami, not far from the campus of Florida International University, says that he conducts much of his business from his home. That power loss not only constrained his ability to keep working but posed a life-or-death situation for his family: Columbie’s 90-year-old grandmother, who lives with him and his girlfriend, depends on electrical power to operate her oxygen pump.
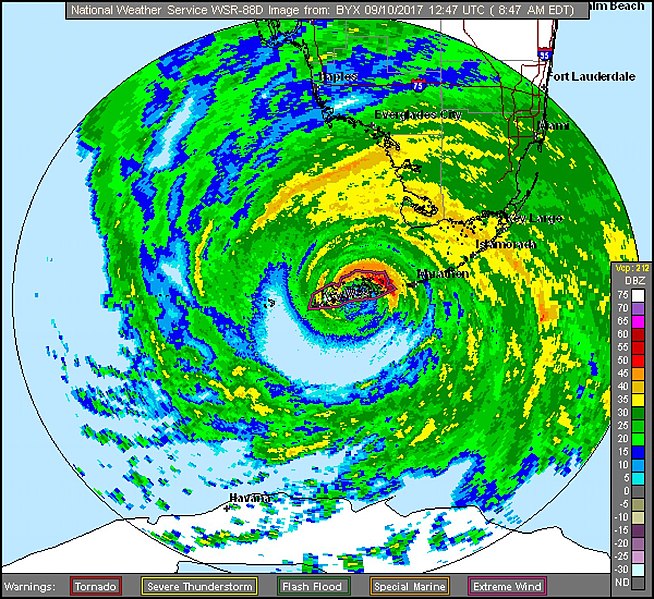 Fortunately, he says, he had a backup generator, the use of which alternated between providing power for his grandmother’s oxygen and the family’s refrigerator. Meanwhile, his roof was leaking and there was six inches of rainwater swamping the house — the water gushing into the kitchen through the laundry room, dishwasher and even the oven.
Fortunately, he says, he had a backup generator, the use of which alternated between providing power for his grandmother’s oxygen and the family’s refrigerator. Meanwhile, his roof was leaking and there was six inches of rainwater swamping the house — the water gushing into the kitchen through the laundry room, dishwasher and even the oven.
While Columbie saw instances of tempers growing short in Miami’s September heat, he was nonetheless cheered by the way his community responded. “Neighbors were coming by to see if I needed gasoline for my generator,” Columbie says. “People were firing up food on their outside grills. There was no air-conditioning or cold showers but we cooled off by jumping in a neighbor’s pool. I saw a lot of people coming together.”
At the same time, he was doing what he could to assist merchants who did business with Axiom. Only one – a retail clothing store in Miami – was permanently shuttered. One of his clients, Oscar Pratt, owner of Odessy Party Supplies in Miami Gardens, was grateful for a moratorium on daily payments.
“We’re in the business of selling party accessories for events from births to funerals and everything in-between,” Pratt says. “Baby showers, christenings, birthdays, quinceaneras, ‘Sweet Sixteens,’ graduations, weddings, and all kinds of themed parties like Halloween,” he says. “We sell plates and cups, candy bags, cake-toppers, small favors, pinatas…”
Pratt said he’d called his funders ahead of the storm and “requested some leeway” from payments. Once the storm hit – and for two weeks afterward while there was no electricity – the party-supply business was pretty much on hold. “We had a few days without electricity or phone,” he says. “We couldn’t open the doors and do business because we use computer-generated receipts. Our customer base was down to just about nothing. Without electricity, people weren’t working and they weren’t having parties.”
Following the two-week grace period, Pratt says that his funders, which included QuarterSpot, granted a second two-week period of leniency in which Odessy was allowed to make reduced payments. “It was very difficult,” he says. “There was no help from FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) or from our insurance company since we’re on high ground and there were no physical damages, just the electricity.”
He reckoned that Odessy, which boasts annual revenues of $1.2 million, was deprived of roughly $50,000-$60,000 in sales because of Irma. Pratt reports that if his lenders had “played hardball” and demanded that he make his payments, he could have stayed in business thanks to “cash on hand” but it wouldn’t have been easy.
Meantime, his lenders’ forbearance was soon rewarded. By October, business was back to normal and he resumed making payments in full. “As soon as the lights went on,” Pratt says, “the parties started again.”
Similarly, says Paul Boxer, chief marketing officer at Quicksilver Capital in Brooklyn, the ultimate impact of Hurricane Irma on his firm’s funding business was to build trust and cement relationships with clients in South Florida. “We had a full team on board to answer the large number of calls coming in and to assist our merchants with any questions they had,” he says.
 Many affected merchants, Boxer reports, were forced to evacuate ahead of the storm. When they returned, it was common for them to discover that their shops and stores sustained flooding damage from the heavy rains and a storm surge. Roofs were blown-off and structures were battered by 100-plus mile-an-hour winds, falling trees, and whipped-up debris. Even businesses that suffered little damage were paralyzed by the loss of electricity, impassable roads, and the absence of customers.
Many affected merchants, Boxer reports, were forced to evacuate ahead of the storm. When they returned, it was common for them to discover that their shops and stores sustained flooding damage from the heavy rains and a storm surge. Roofs were blown-off and structures were battered by 100-plus mile-an-hour winds, falling trees, and whipped-up debris. Even businesses that suffered little damage were paralyzed by the loss of electricity, impassable roads, and the absence of customers.
“Some were down for a few days,” Boxer reports. “Some were down a month to two months. We kept in touch. We were really on top of things with our merchants and asking them what they needed. We even fielded general safety questions and directed them on whom to call with insurance questions and other related business questions. It was good business,” he adds, “because it showed you cared. We were looking to do the right thing by our merchants and they appreciated it.”
Quicksilver typically offered merchants a two-to-three week “reprieve” on payments, Boxer says. For those businesses and entreprenuers whose operations were “completely out of commission” and needed more time, he says, the company suspended payments for as long as two months.
In the end, Quicksilver’s policy of forbearance reaped dividends. It not only built up good will with its customer base but also with the Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) who’d brokered many of the firm’s Florida deals. “We helped grow that relationship,” Boxer says of the merchant-ISO connection. “They (ISOs) love getting renewals. It’s been a win-win for everybody.”
Doug Rovello, senior managing partner at Fund Simple, Inc., an alternative business lender and broker in Palm Harbor, a beach town just outside Tampa, says the Tampa-St. Petersburg area was spared from severe flooding but “we did experience power outages.” Among his clients, he reports, businesses in the food industry were among the most vulnerable. “I had one restaurant that lost $200,000 in business in the month of September,” he says.
 When the electricity went down, grocery stores and bodegas, restaurants, bars, pizzerias, sub shops, delis and luncheonettes suffered outsized losses. Without power, businesses in the food industry were forced to dump spoiled meat, rotting fish, unusable dishes like appetizers and other foodstuffs requiring refrigeration.
When the electricity went down, grocery stores and bodegas, restaurants, bars, pizzerias, sub shops, delis and luncheonettes suffered outsized losses. Without power, businesses in the food industry were forced to dump spoiled meat, rotting fish, unusable dishes like appetizers and other foodstuffs requiring refrigeration.
Rovello reports that the hurricane managed to bollix up the business of one top client, a leading ticket broker in the area with a reputation for obtaining “exclusive” tickets to major events such as A-list rock concerts and featured sporting contests – including the Super Bowl. “He buys tickets in advance and when one big event was canceled he got stuck with $30,000 in tickets that he had to eat,” Rovello says.
Other kinds of businesses that depend on alternative lenders and got hit hard from the loss of power, Rovello observes, were medical clinics, doctors’ offices, pain-management centers, and assisted-living quarters – particularly those south of Sarasota. A number of golf courses also closed down for a couple of weeks, Rovello notes, further impairing the tourism and entertainment economy. “They were not allowed to move any of the damage that was done – poles, trees, et cetera until FEMA got there,” he says.
For some 30 days following Irma’s arrival, Rovello reports that he asked clients to make modest payments – perhaps $100 instead of a $750 monthly payment — “to keep their accounts active.” He also used his connections with FEMA adjusters and interceded with funders on behalf of clients– and even businesses that were not clients – who found themselves in arrears.

While many Floridians were seeking higher ground or hightailing it out of state, Jay Bhatt, who is a senior vice president of marketing at Breakout Capital in McLean, Va., was catching one of the last Jet Blue flights into Orlando to help out his aging parents. They are now in their late 60s and 70s, he reports, and living in a retirement community in Polk County, about ten miles south of Disney World.
Irma was still a Category 1 hurricane with 100 mph winds when it hit Orlando. The electrical grid went down, but Bhatt was able to purchase a generator – the kind designed specifically to provide electricity for oxygen respirators — from Home Depot. During his stay, Bhatt made several car trips in search of fuel, each of which took him probably 35-40 minutes. “We also leveraged some of the neighbors’ sockets,” he says, “but they were so small that the wattage only allowed for the operation of the fridge and a fan.”
Electricity was restored after four or five days. “The fact that it was a retirement community might have been why we got power back so soon while it took two or three weeks for many others,” he reckons.
 While Bhatt’s attention was focused on his parents, his employer – which had just offered a blanket hold on payments to its merchant accounts in 11 Texas counties that had been simultaneously inundated and walloped by Hurricane Harvey – now faced the challenge of responding to the second hurricane in two weeks. With Irma, Breakout chose to deal with its customers individually. “We didn’t do an immediate blanket response” as in Texas, Bhatt says, adding: “We were able to contact each one and we only wrote off one small business.”
While Bhatt’s attention was focused on his parents, his employer – which had just offered a blanket hold on payments to its merchant accounts in 11 Texas counties that had been simultaneously inundated and walloped by Hurricane Harvey – now faced the challenge of responding to the second hurricane in two weeks. With Irma, Breakout chose to deal with its customers individually. “We didn’t do an immediate blanket response” as in Texas, Bhatt says, adding: “We were able to contact each one and we only wrote off one small business.”
Rakem Lampkin, senior customer service representative at Pearl Capital, a New York-based alternative funder, says that his firm funds “roughly 175” businesses in South Florida. In addition to those establishments already mentioned as economically reeling because of Irma, such as restaurants, he cited “car dealerships, automotive repair shops and tech companies” as among the hardest hit, especially from the lack of electricity.
Lampkin also noted that many of Pearl’s merchants felt Irma’s wrath when colleges and state schools closed their doors. “Everything from transportation, lunches, sports equipment, even mom-and-pop florists” were slammed, he says, adding: “When the schools shut down, our payments slowed down.”
Pearl provided preferential treatment to merchants on the coast who were granted “a hold on debit payments,” Lampkin says. Even for coastal businesses that remained “structurally sound,” the business owners’ and employees’ “homes were affected, which kept them from getting to work,” he says.
As for businesses situated inland, “We were still sympathetic,” Lampkin says, but after an initial five-day grace-period their discounts were in the range of 66%-75% “so that we could focus our resources toward the people on the coast.”
To monitor the situation from New York, Lampkin says, the company was able to rely on accounts in the local news media, Google Maps, and other Internet sources. “We evaluated the situation case-by-case and week-by-week,” he says.
Jennifer Legg, a co-owner of Rochelle’s Jewelry & Watch Repair at the Indian River Mall in Vero Beach, is a Pearl-funded merchant who says she shut down the family-run business “for six or seven days” after Irma while the electricity went out. “Trees were down and a lot of people lost food and trailers, but we were not impacted as much as we were supposed to be,” she remarked.
Most of the shop’s business consists of customers stopping in for a new battery or a watch-band. Once they’re in the store, there’s a chance that they’ll purchase something else. But Irma put the kibosh on mall traffic. “A lot of people left the state, so that hurt business,” Legg says.
The store – which records annual sales of about $200,000 — lost probably $10,000 in revenue because of Irma. “It was very hard for that month of September,” Legg says. “Even after the doors opened, it was dead. No money came in for about two weeks.”
Fortunately, though, her capital source “did not take money out for a week,” she says. “If they’d kept taking it out,” she added, “we would have defaulted.”
Catching Up With Online Lending – A Timeline
October 21, 20177/17
- Online lender Upgrade, launched by former Lending Club CEO Renaud Laplanche, revealed it had already hired about 100 people
- Credit risk startup James closed $2.7M funding found led by Gaël de Boissard
7/18 – Former Bizfi COO Tomo Matsuo joined iPayment as an SVP to oversee its new merchant cash advance division
7/21 – SoFi Chief Revenue Officer Michael Tannenbaum departed the company
7/27
- Lending surpassed $500M in lifetime originations
- RealtyShares acquired marketplace platform Acquire Real Estate
7/28
- Former MB Financial Bank SVP Stan Scott became VP at Gibraltar Business Capital
- Prosper Marketplace shut down its Prosper Daily (formerly BillGuard) app
7/31 – First Associates Loan Servicing announced the opening of their new 1000-seat capacity operations center in Baja California, Mexico
8/1
- Ron Suber joined Credible.com as executive vice-chairman and a member of the board of directors
- PeerStreet integrated with Personal Capital
8/2
- Lending Loop raised $2M, launched automated investment platform
- PeerIQ secured $12M in Series A round
- OnDeck partnered with Payment Source in Canada
- Bread raised $126M in equity and debt
8/3 – Kabbage secured $250M in Series F round from SoftBank Group, was valued at more than $1.25B
8/9
- Former Capital One VP Heather Tuason became Chief Product Officer at StreetShares
- PayPal acquired Swift Capital
8/10 – Coinbase raised $100M at $1.6B valuation
8/11 – Former SoFi employee raised Brandon Charles filed a lawsuit against the company alleging among other things that he witnessed sexual harassment in the workplace
8/14
- Prosper closed $500M securitization, announced $775M in Q2 loan originations, $41.4M net loss
- Bitcoin surged past $4,000
8/15 – iPayment announced the formation of its new merchant cash advance division, iPayment Capital
8/16 – Fifth Third Bank made another equity investment in ApplePie Capital, agreed to purchase loans through the company’s marketplace
8/19 – Former CFO of Credibly became president of Western Funding
8/22 – Former SoFi employees filed a lawsuit against the company over wage issues
8/23 – Ellevest raised $32.5M
8/24 – AutoFi raised $10M in Series A
8/25 – Rep. Maxine Waters called for a congressional hearing on SoFi’s bank charter application and ILC charters in general
8/29 – Snap Finance secured $100M credit facility
8/30
- IOU Financial announced Q2 originations of $26.2M (US) and a net loss of $2.08M (CAD)
- ShopKeep launched ShopKeep Capital, a merchant cash advance service
8/31 – Bizfi wound down operations, sold servicing rights to its $250M portfolio to Credibly
9/2 – Bitcoin surpassed $5,000
9/5 – Former Chief Sales Officer of OnDEck, Paul Rosen, joined CoverWallet as COO
9/6 – Square revealed that they would apply for an ILC charter, following in the footsteps of SoFi
9/7
- Former Director of External Sales at OnDeck, Jared Kogan, joined Pearl Capital as Chief Revenue Officer
- First Internet Bank announces strategic partnership with Lendeavor, Inc.
9/11
- SoFi CEO Mike Cagney announced he had resigned as board chairman and would be resigning as CEO later in the year
- Lenda raised $5.25M Series A
9/12
- Groundfloor announced $100M loan purchase agreement with Direct Access Capital
- Orchard unveiled its Deals platform
- JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon called Bitcoin a fraud for stupid people
9/13 – dv01 closed $5.5M Series A
9/14 – SmartBiz surpassed $500M in lifetime SBA loan originations
9/15
- Amid more negative press, SoFi CEO Mike Cagney announced he was resigning as CEO immediately
- Enova announced $25M share repurchase program
9/20 – World Business Lenders acquired strategic assets of Bizfi including the company’s brand and marketplace
9/22 – Prosper Marketplace raised $50M in a Series G round at a 70% lower valuation of $550M
See previous timelines:
5/17/17 – 7/11/17
4/6/17 – 5/16/17
2/17/17 – 4/5/17
12/16/16 – 2/16/17
9/27/16 – 12/16/16





























